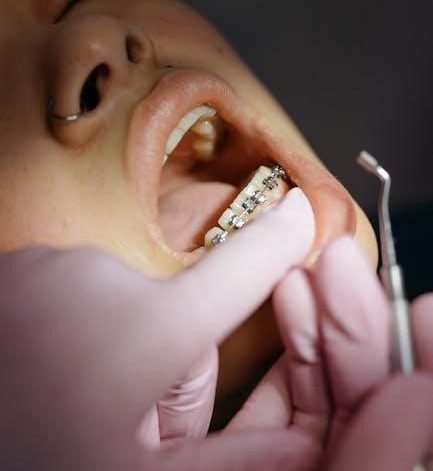
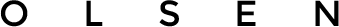Dental Instruments: A Comprehensive Guide with Pictures and Names
Recent advancements in AI-driven cybersecurity, like 7AI’s $130M Series A funding, demonstrate innovative approaches to complex tasks, mirroring the precision needed in dental procedures.
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence, as exemplified by 7AI’s substantial $130 million Series A funding round and $700 million valuation, highlights a paradigm shift towards automated systems. This mirrors the intricate world of dental instruments, where precision and specialized tools are paramount.
Dental instruments, encompassing a vast array of designs and functionalities, are essential for diagnosing, treating, and preventing oral diseases. Understanding these tools – their specific names, appearances, and applications – is crucial for dental professionals and students alike. A comprehensive guide, often available as a PDF resource, provides detailed visuals and descriptions, aiding in proper identification and utilization.
Importance of Knowing Dental Instruments

The recent $130M Series A funding for 7AI, an AI agent building company focused on cybersecurity alert triage, underscores the value of efficient and accurate systems. Similarly, a thorough understanding of dental instruments is vital for effective patient care. Misidentification or improper use can lead to inaccurate diagnoses, ineffective treatments, and potential patient harm.
A detailed resource, such as a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guide, facilitates correct instrument selection and technique. This knowledge empowers dental professionals to deliver optimal oral health outcomes, mirroring the improved security outcomes promised by AI-driven solutions like 7AI.
Classification of Dental Instruments
Just as 7AI utilizes AI agents to categorize and address cybersecurity threats, dental instruments are systematically classified based on their function. Broadly, they fall into categories like operative, restorative, periodontal, surgical, and diagnostic instruments. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resource typically organizes instruments this way.
Understanding these classifications – and the specific instruments within each – is crucial for efficient treatment planning. This systematic approach, akin to 7AI’s triage system, ensures the correct tool is readily available for each procedure, optimizing workflow and patient care.
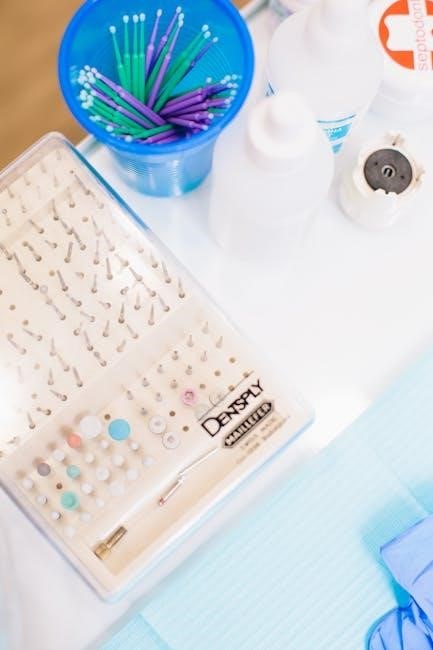

Basic Operative Dentistry Instruments
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents handling repetitive cybersecurity tasks, basic operative instruments facilitate fundamental dental procedures, detailed in ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guides.
Hand Instruments for Operative Dentistry
Reflecting 7AI’s focus on automating security workflows with AI agents, hand instruments in operative dentistry represent the foundational tools for direct clinical intervention. These instruments, meticulously detailed in resources like ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’, require manual dexterity and precise control. They encompass a diverse range, including explorers, excavators, and carriers, each designed for specific tasks such as caries detection, removal, and material manipulation.
Understanding their form, function, and proper handling – as illustrated in comprehensive guides – is crucial for achieving optimal treatment outcomes and minimizing patient discomfort. The availability of detailed visual references, such as those found in PDF guides, significantly aids in instrument identification and correct application.
Explorer Instruments
Similar to 7AI’s agents triaging cybersecurity alerts, explorer instruments are the initial diagnostic tools in operative dentistry. Resources like ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ showcase their varied designs – spoon, contra-angle, and others – each optimized for detecting caries, calculus, or enamel defects. These instruments don’t remove decay; they locate it.
Proper technique involves light pressure and a sweeping motion, allowing tactile and visual assessment of tooth surfaces. Accurate identification, aided by visual guides, is paramount for effective treatment planning and avoiding unnecessary intervention. Mastering explorer use is fundamental to conservative dentistry.
Types of Explorers (e.g., Spoon, Contra-angle)
Reflecting 7AI’s diverse AI agents handling security workflows, explorers come in distinct forms. Spoon explorers, with rounded tips, are ideal for broad surface assessments, as detailed in ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’. Contra-angle explorers, featuring angled blades, excel in accessing posterior teeth and tight interproximal spaces. Other types include sickle explorers for detecting overhangs and cast restorations.
Selecting the appropriate explorer depends on tooth location and clinical need. Understanding each type’s advantages, often visualized in downloadable guides, ensures thorough and accurate caries detection, mirroring the precision of AI-driven threat investigation.
Excavator Instruments
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents triaging cybersecurity alerts, excavators meticulously remove caries and debris. These instruments, detailed in ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’, feature blades designed for efficient material removal while minimizing healthy tissue disturbance. Spoon excavators are versatile for larger excavations, while angle excavators access difficult-to-reach areas.
Proper technique, guided by visual aids, is crucial. Excavators require controlled pressure and careful angulation to prevent pulpal exposure. Mastering their use, like AI mastering threat analysis, is essential for successful restorative procedures and patient comfort.
Types of Excavators (e.g., Spoon, Angle)
Types of Excavators (e.g., Spoon, Contra-angle)
Reflecting 7AI’s diverse AI agent capabilities, excavators come in various designs. Spoon excavators, as depicted in ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’, possess rounded blades for general caries removal. Angle excavators, with their angled blades, excel in accessing proximal cavities and tight spaces. Contra-angle excavators offer enhanced precision and control.
Selecting the appropriate excavator depends on cavity morphology and accessibility. Proper identification, aided by visual guides, ensures efficient and conservative caries excavation, mirroring the targeted approach of AI-driven cybersecurity solutions.
Carriers and Burnishers
Similar to 7AI’s platform handling security workflows, carriers and burnishers play crucial roles in restorative procedures. Carriers, often illustrated in ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’, transport materials like amalgam or composite into the prepared cavity. Burnishers, with their smooth, rounded ends, condense and adapt restorative materials against cavity walls.
These instruments ensure proper material placement and adaptation, contributing to long-lasting restorations. Understanding their function, as detailed in visual guides, is vital for achieving optimal clinical outcomes, much like AI agents optimizing cybersecurity responses.
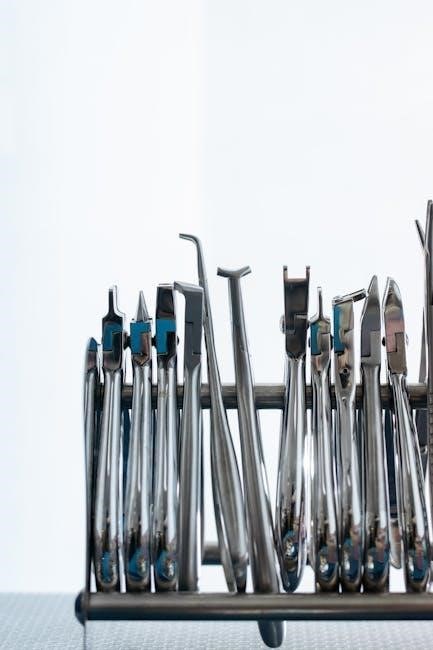
Restorative Dentistry Instruments
Reflecting 7AI’s AI agent innovation, restorative instruments, detailed in ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’, rebuild tooth structure with precision and efficiency.
Amalgam Instruments
Similar to 7AI’s triage of cybersecurity alerts, amalgam instruments require a systematic approach for successful restorations. Detailed within comprehensive resources like ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’, these tools are specifically designed for handling amalgam material. Amalgam carriers efficiently transport the alloy to the prepared cavity, while condensers firmly pack and compress it, ensuring a dense, durable fill.
Understanding the precise function of each instrument – from spoon-shaped carriers to various condenser designs – is crucial for achieving optimal results. These instruments, when used correctly, contribute to long-lasting and reliable dental restorations, mirroring the efficiency of AI-powered security solutions.
Amalgam Carriers
Reflecting 7AI’s ability to consume zero-day alerts, amalgam carriers efficiently ‘consume’ and deliver amalgam alloy to the tooth preparation. Resources like ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ visually detail various carrier designs – typically spoon-shaped – optimized for holding and transferring the material. These instruments are not for condensing; their sole purpose is precise placement.
Proper carrier technique minimizes waste and contamination, ensuring the amalgam reaches the cavity without disruption. Mastering this initial step, akin to accurate threat identification in cybersecurity, is fundamental for a successful and durable restoration, showcasing the importance of specialized tools;
Amalgam Condensers
Similar to 7AI’s handling of repetitive tasks with AI agents, amalgam condensers compact the placed amalgam within the cavity preparation. ‘Dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resources illustrate diverse condenser shapes – round, oval, and flame – each suited for specific areas. Condensation eliminates voids and increases the material’s density, enhancing its strength and longevity.
Effective condensation, much like a robust cybersecurity system, requires methodical technique and appropriate instrument selection. This process ensures a tightly packed restoration, resisting fracture and providing a durable, long-lasting result, mirroring the security outcomes 7AI delivers.
Composite Instruments
Reflecting 7AI’s innovative approach to security workflows, composite instruments facilitate precise placement and sculpting of tooth-colored restorations. ‘Dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guides showcase fillers for initial placement, sculptors for contouring, and burnishers for smoothing. These instruments, like AI agents triaging alerts, demand finesse and control.
Successful composite restorations rely on layering techniques and meticulous adaptation, mirroring the layered security approach of modern cybersecurity. Proper instrument selection and technique are crucial for achieving esthetic and functional results, ensuring a seamless blend with the natural tooth structure.
Composite Instruments (e.g., Fillers, Sculptors)
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents handling repetitive security tasks, composite fillers efficiently introduce material, while sculptors refine contours. ‘Dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resources detail various instrument shapes – leaf, flame, and spoon – each serving a specific purpose. Fillers pack composite into cavities, while sculptors shape and define the restoration’s anatomy.
These instruments, like the tools used in threat investigation, require skilled manipulation. Achieving natural aesthetics and proper occlusion depends on precise instrument control and understanding composite material properties, mirroring the need for accuracy in cybersecurity.
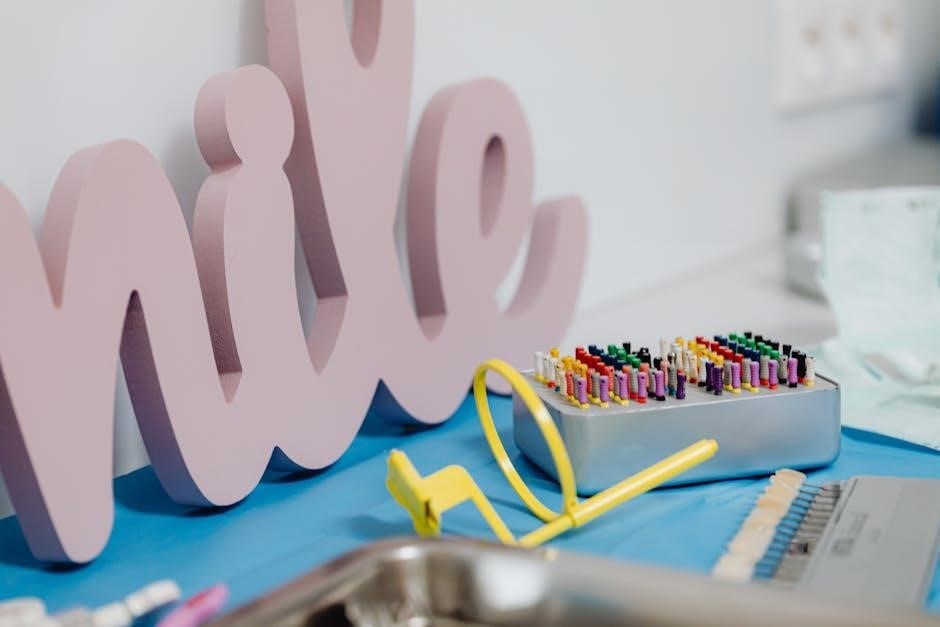

Periodontal Instruments
Reflecting 7AI’s triage of cybersecurity alerts, periodontal tools target localized issues. ‘Dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guides showcase scalers and probes for gum health assessment.
Scaling and Root Planing Instruments
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents handling repetitive cybersecurity tasks, scaling and root planing instruments address recurring periodontal issues with focused precision. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resource will detail hand scalers – including sickle and curette varieties – essential for removing calculus and smoothing root surfaces.
Furthermore, these guides illustrate power-driven scalers, like ultrasonic scalers, offering efficient debris removal. Understanding the specific designs and applications of each instrument, as visualized in these PDFs, is crucial for effective periodontal therapy and maintaining optimal patient oral health. Proper identification aids in accurate treatment planning.
Hand Scalers (e.g., Sickle, Curette)
Reflecting 7AI’s focus on automating alert triage, hand scalers represent a foundational, manually-driven approach to periodontal care. A detailed ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ will showcase sickle scalers, designed for removing supragingival calculus with sweeping motions. Conversely, curettes, with their pointed tips, access subgingival areas for root planing.
These PDFs visually differentiate blade shapes (universal, Gracey) and shank designs, crucial for adapting to varying tooth surfaces. Mastering hand scaler techniques, aided by clear visual guides, ensures effective calculus removal and promotes healthy periodontal tissues, mirroring the precision of AI-driven security solutions.
Power-Driven Scalers (e.g., Ultrasonic Scalers)
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents handling repetitive cybersecurity tasks, power-driven scalers automate calculus removal. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ illustrates ultrasonic scalers utilizing high-frequency vibrations to fragment and flush away deposits. These instruments minimize hand fatigue and offer efficient scaling, particularly for heavy calculus.
PDF resources detail various tip designs (slim, chisel) and power settings, impacting effectiveness and safety. Understanding these nuances, visually presented, is vital. Like AI’s ability to investigate novel threats, power scalers enhance precision and speed in periodontal treatment, improving patient outcomes.
Periodontal Probes
Reflecting 7AI’s triage of cybersecurity alerts, periodontal probes assess the state of gingival tissues and periodontal pockets. A ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ showcases probe markings (millimeters) for accurate depth measurements. These probes, crucial for diagnosis, identify areas of inflammation and attachment loss, similar to AI flagging potential security breaches.
PDF guides detail proper probing technique – walking the probe along the tooth surface. Variations exist (Williams, Marquis), each suited for specific clinical needs. Like AI’s analytical capabilities, precise probing provides essential data for treatment planning and monitoring periodontal health.
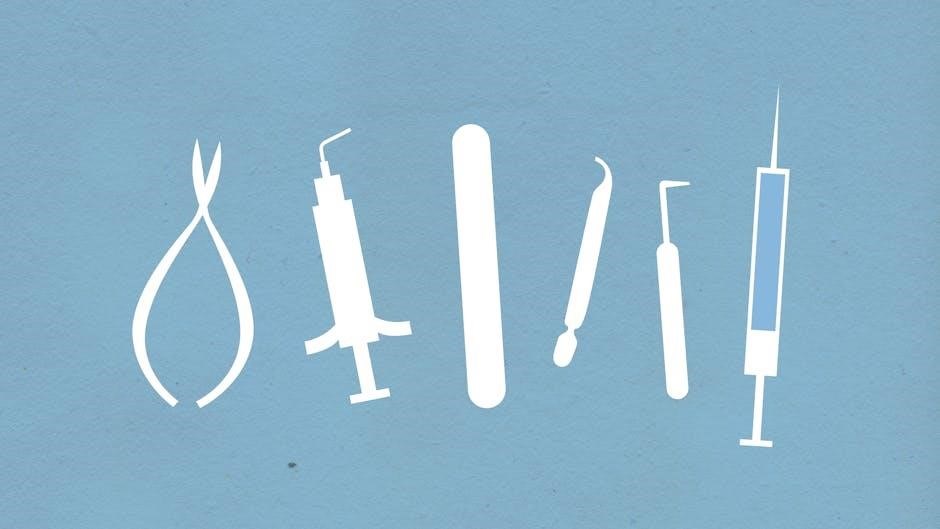
Surgical Instruments
Mirroring 7AI’s handling of complex cybersecurity tasks, surgical instruments demand precision; a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ illustrates forceps and elevators for extractions.
Extraction Forceps
Just as 7AI’s AI agents triage cybersecurity alerts with efficiency, extraction forceps are designed for the targeted removal of teeth. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ will detail various types, categorized by jaw shape and function. Upper forceps typically feature narrower beaks for accessing molars, while lower forceps have broader beaks to accommodate the mandible’s curvature.
Understanding these distinctions, visually represented in such a guide, is crucial. Forceps come in different sizes and designs – for example, Bayonet, Covey, and Jersey forceps – each suited for specific clinical scenarios. Proper selection and technique, guided by detailed illustrations, minimize trauma and ensure successful extractions.
Types of Extraction Forceps (e.g., Upper, Lower)
Similar to 7AI’s platform handling diverse cybersecurity threats, extraction forceps address varied tooth removal needs. A detailed ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ showcases upper forceps – often slender, angled for molar access – and lower forceps, broader to fit the mandible. Bayonet forceps, with long beaks, target deeply rooted teeth.
Covey forceps feature cross-hatched jaws for enhanced grip. Jersey forceps are universal, adaptable for multiple extractions. Visual guides are essential for identifying each type, understanding jaw angulation, and selecting the appropriate instrument for optimal force application and minimal patient discomfort, mirroring AI’s precise triage.
Elevators
Reflecting 7AI’s AI agents handling repetitive cybersecurity tasks, dental elevators efficiently loosen teeth before extraction. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ details straight elevators, used for initial luxation, and Coupland elevators, angled for accessing difficult-to-reach roots.
Cryer elevators, with curved blades, navigate around adjacent teeth. Winter elevators offer a delicate approach for fragmented roots. Proper technique, guided by visual references, minimizes trauma. Selecting the correct elevator, based on tooth position and root morphology, is crucial for controlled elevation, mirroring AI’s strategic threat investigation.
Types of Elevators (e.g., Straight, Coupland)
Similar to 7AI’s platform handling security workflows, dental elevators come in specialized forms. A ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ showcases straight elevators for initial tooth loosening, providing direct upward force. Coupland elevators, angled at 90 degrees, access buccal and lingual root surfaces effectively.
Cryer elevators, with curved blades, navigate around adjacent teeth, while Winter elevators are designed for delicate root fragment removal. Understanding each type’s application, as detailed in visual guides, ensures controlled luxation and minimizes potential damage, mirroring AI’s precise alert triage.
Surgical Scalpels
Reflecting 7AI’s ability to investigate novel threats, surgical scalpels in dentistry demand precision. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ illustrates various blade shapes – #10, #11, #12, and #15 – each suited for specific soft tissue incisions. Scalpel handles are often detachable, allowing blade changes for versatility.
Proper technique, guided by detailed visuals, minimizes trauma and promotes optimal healing. Like AI agents handling repetitive tasks, skilled scalpel use streamlines surgical procedures, ensuring clean, controlled incisions essential for successful outcomes and patient comfort.
Endodontic Instruments
Similar to 7AI’s triage of cybersecurity alerts, endodontic instruments require meticulous selection, as detailed in a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guide.
Files
Reflecting the sophisticated agentic AI of companies like 7AI, endodontic files demand precise application for effective canal shaping and cleaning. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resource is crucial for identification. These instruments, available in varying tapers and lengths, navigate complex root canal systems.
Understanding file characteristics – from tip size to blade configuration – is paramount. K-files, with their cutting edges, and H-files, designed for irrigation, represent fundamental types. Proper file sequencing and technique, as illustrated in detailed guides, minimize procedural errors and maximize treatment success. Mastery requires diligent study and practical application.
Types of Endodontic Files (e.g., K-files, H-files)
Similar to 7AI’s triage of cybersecurity alerts, endodontic files categorize by function. A ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ should clearly delineate these. K-files, possessing a cutting edge on all four sides, excel at initial canal negotiation and shaping. Conversely, H-files feature a helical cutting pattern, ideal for irrigation and debris removal.
Understanding taper and tip size is vital; these parameters dictate file flexibility and cutting efficiency. NiTi files, offering superior flexibility, are also commonly used. Proper selection, guided by radiographic assessment, ensures safe and effective root canal preparation, mirroring the precision of AI-driven analysis.
Reamers
Echoing 7AI’s focus on threat investigation, reamers play a crucial role in root canal shaping. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ must detail their unique design. Unlike files, reamers have an intermittent cutting pattern – cutting edges are present, but not continuous around the shank. This design facilitates efficient debris removal and canal widening.
They are particularly useful for establishing glide paths and preparing coronal portions of canals. Reamers are often used in a step-back technique, progressively enlarging the canal. Careful technique prevents ledging or transportation, ensuring preservation of the root canal anatomy, much like precise cybersecurity protocols.
Spreaders and Pluggers
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents handling repetitive tasks, spreaders and pluggers efficiently manage obturation during root canal treatment. A detailed ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ should illustrate their varied tapers and shapes. Spreaders condense gutta-percha laterally, creating space for additional material. Pluggers, conversely, vertically condense the gutta-percha, ensuring a dense, apical seal.
These instruments are crucial for achieving a hermetic seal, preventing bacterial re-infection. Proper technique, guided by radiographic confirmation, is paramount. Like cybersecurity’s layered defenses, a well-executed obturation provides long-term endodontic success.
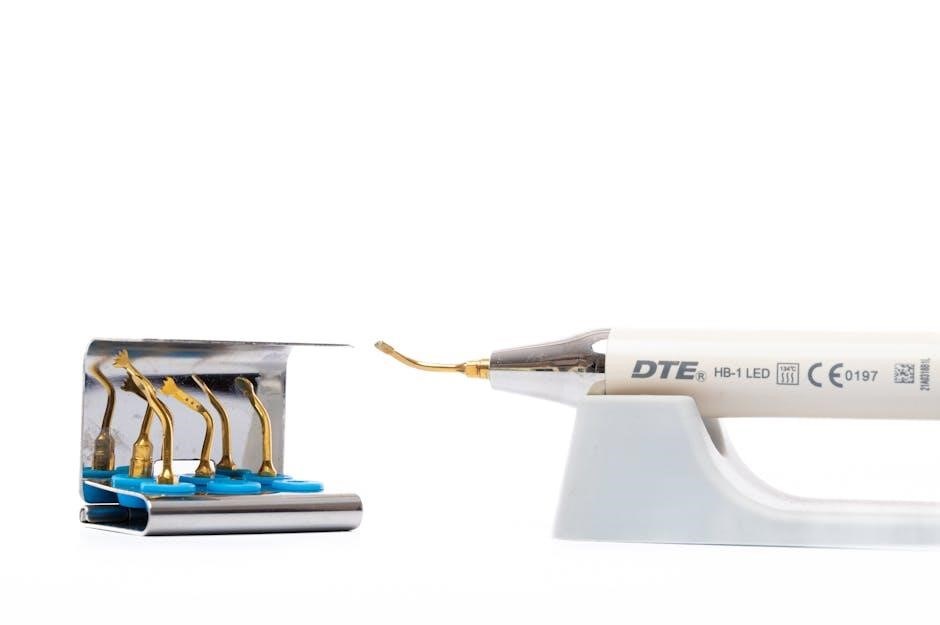

Diagnostic Instruments
Reflecting 7AI’s alert triage, diagnostic tools like mouth mirrors and probes aid in identifying dental issues; a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ is helpful.
Mouth Mirrors
Similar to how 7AI analyzes cybersecurity alerts, mouth mirrors are essential diagnostic tools, reflecting light onto surfaces otherwise difficult to view directly; These instruments, often included in a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guide, come in various shapes and sizes – round, oval, and rectangular – to accommodate different clinical situations and patient anatomy. They aid in visualization during examinations, assisting in detecting caries, observing soft tissue abnormalities, and retracting the tongue or cheeks for improved access.
High-quality mirrors provide clear, undistorted images, crucial for accurate diagnosis. Proper handling and sterilization are paramount, mirroring the security protocols 7AI employs.
Dental Probes
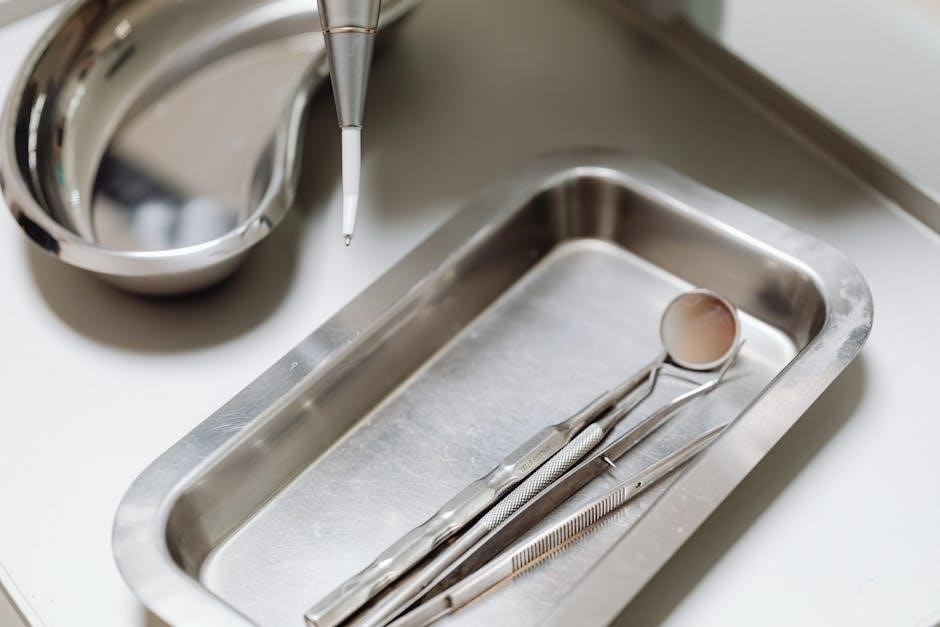

Just as 7AI triages cybersecurity alerts with AI agents, dental probes are vital for assessing periodontal health. Commonly featured in a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resource, these instruments have a tapered, pointed tip used to measure pocket depths, locate furcation involvements, and detect calculus deposits. Different probe designs – such as Williams, Marquis, and UNC-15 – offer varying features for specific clinical needs. Accurate probe readings are essential for diagnosing and monitoring periodontal disease progression, much like 7AI’s threat investigation.
Sterilization is critical for preventing cross-contamination.
Bite-Wing Holders
Similar to how 7AI streamlines security workflows with AI agents, bite-wing holders optimize radiographic procedures. Frequently illustrated in a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guide, these devices securely position bite-wing film or digital sensors within the patient’s mouth. They ensure consistent angulation and stabilization, crucial for diagnostic image quality. Various designs – including plastic and metal options – accommodate different patient sizes and preferences. Proper use minimizes distortion and retakes, enhancing efficiency, mirroring 7AI’s focus on delivering better security outcomes through automation.
Sterilization protocols must be followed diligently.
Additional Instruments
Reflecting 7AI’s platform approach to cybersecurity, modern dentistry utilizes diverse tools, often detailed in a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ resource for clarity.
High-Speed Handpieces
Similar to 7AI’s AI agents automating security tasks, high-speed handpieces dramatically increase efficiency in restorative dentistry. These instruments, frequently illustrated in a ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ guide, utilize a turbine driven by compressed air to rotate burs at exceptionally high speeds – typically 300,000 to 400,000 rpm.
This allows for rapid removal of tooth structure during cavity preparation and finishing procedures. Different bur shapes and sizes are employed, each serving a specific purpose. Proper understanding, often aided by visual references, is crucial for controlled and precise tooth preparation, mirroring the strategic focus 7AI brings to cybersecurity.
Low-Speed Handpieces
Reflecting 7AI’s handling of repetitive cybersecurity tasks, low-speed handpieces perform a diverse range of functions requiring controlled power. A ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ will showcase these versatile tools, operating at speeds between 3,000 and 30,000 rpm. They are essential for procedures like polishing restorations, removing cement, and applying finishing touches.
Attachments like prophy cups, brushes, and diamond burs expand their utility. Unlike high-speed handpieces, low-speed versions offer greater tactile control, crucial for delicate work. Mastering their use, aided by visual guides, is fundamental for achieving optimal clinical outcomes, much like strategic security operations.
Light Curing Units
Similar to 7AI’s rapid threat investigation, light curing units swiftly polymerize composite resins and adhesives. A comprehensive ‘dental instruments pictures and names pdf’ should detail these devices, utilizing blue light within a specific wavelength (typically 400-500 nm). They are indispensable for modern restorative dentistry, ensuring durable and aesthetically pleasing results.
Variations include LED, halogen, and quartz tungsten halogen (QTH) units, each with unique characteristics. Proper technique – distance, exposure time, and light intensity – is vital for complete polymerization. Understanding these parameters, visually demonstrated in guides, parallels the precision needed in cybersecurity alert triage.